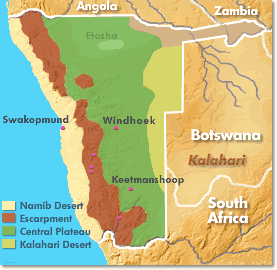
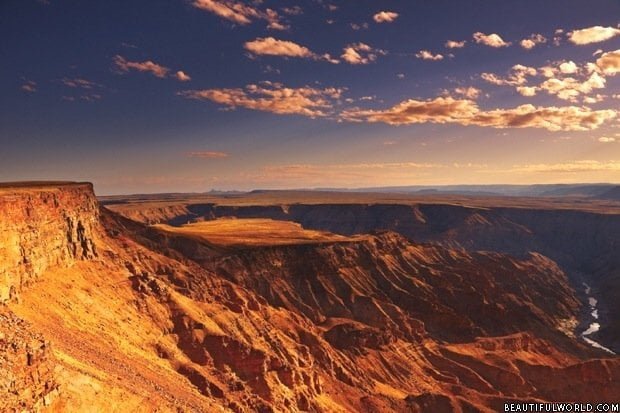
Covering an area of 31,274 sq. mi (81,000 sq. km), the Namib is a coastal desert, situated along the south-western coast of the African continent. Stretching over 1200mi (2000km), the Namib crosses Angola, Namibia and South Africa. Characterised by red sand dunes that can reach impressive heights, the Namib is considered to be particularly old, even by geological standards.
Namib Desert Map
Interesting Facts About the Namib Desert
The word ‘Namib’ is of Nama origin, and means ‘open space’. Geologists believe that the Namib Desert is the world’s oldest desert. It is thought that an arid climate began to dominate in the region approximately 55 million years old, before changing to a semi-arid climate 14-18 million years ago.
Namib Desert Climate
The Namib experiences less than 1cm of rain annually and is almost entirely barren. Strangely, whilst the region is virtually rainless, its air is typically at or near to saturation point, and fog is very common. The coastal regions have a steady temperature throughout the day and seasons of 9-20C.The wind blows inland pushing moisture ladened air from the sea inland forming thick fog and providing plants and wildlife with a rare reliable water source.

Inland temperatures vary much more and they can be freezing overnight and reach 45C during daylight hours. Rainfall is rare along the coast and central regions of the desert but it increases as the desert rises towards the towering Great Escarpment at its rear. Many streams run from this rock formation back through the desert towards the sea. Few reach it as they evaporate or soak below the desert. These water reserves are tapped to support the deserts few towns.
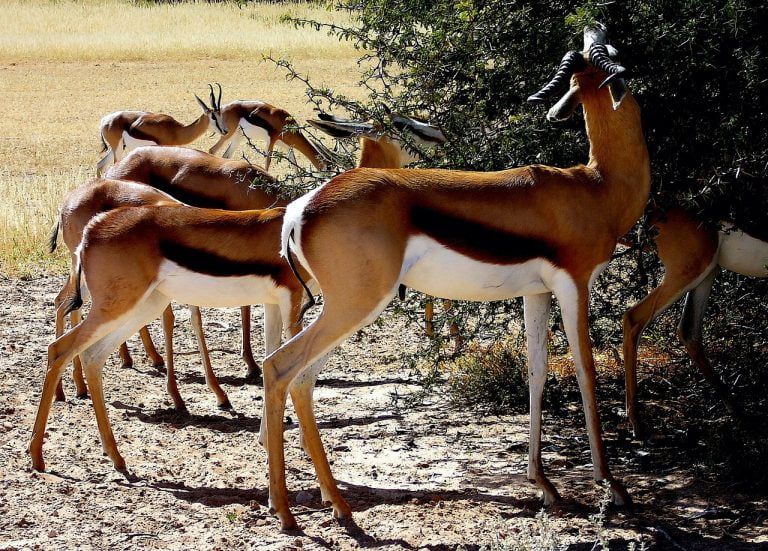
Namib Desert Animals
Whilst there are other coastal deserts (such as the Atacama) bounded by cool ocean currents, the Namib is the only one in which endemic plants and animals have evolved in virtually barren dunes. In fact, the Namib is teeming with animals, including elephants, rhinos, Hartmann’s zebra, lions, gemsbok and the black-faced impala.

Namib Desert Plants
A number of rare and interesting plants are present in the Namib Desert, such as the Welwitschia Mirabilis, which consists only of 2 leaves and a stem, and is estimated to reach up to 2000 years old. It can grow up to 6-feet high, and 24-feet wide, and was referred to by Darwin as the ‘the platypus of the plant kingdom’.
Another bizarre plant is the Quiver Tree, which effectively cuts off its own branches in times of severe drought in order to save moisture loss through its leaves.

Protected Areas of the Namib Desert
The Namib is well-protected by a range of national parks, such as the Namib-Naukluft National Park (19,215 sq. mi / 49,768 sq. km) which protects the central area of the region. In fact most of the desert is covered by some level of protection as can be seen by the map below. In 2012 a stretch if the coastal desert was designated a World Heritage site – The Namib Sand Sea.

Diamonds in the Namib Desert
Diamonds are the most important mineral asset found in the Namib Desert. Due to the lightweight nature of diamonds and the ease of theft, the entire region where the diamonds are situated has been declared a Prohibited Area, totally closed to public access.
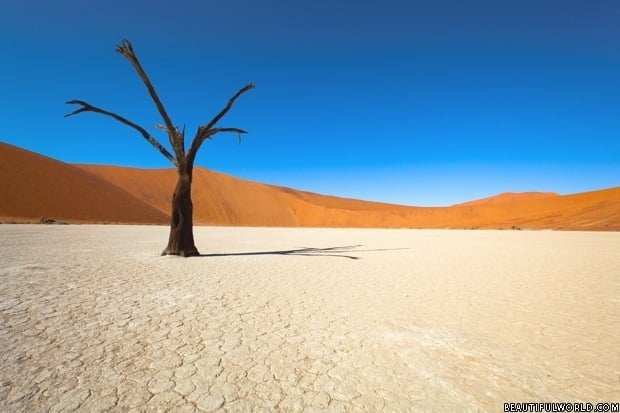
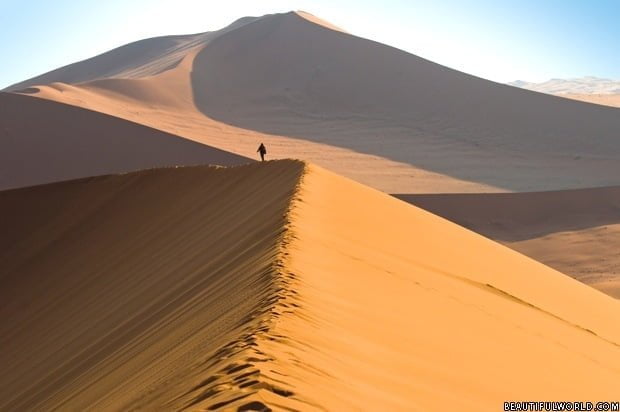
The Namib is home to the highest sand dunes in the world; some of which can reach over 1280ft (390m) high and can even be seen from space.










November 2017 is the month of the desert Ultra challenge. A 250km race through the Namib desert. You have to run through searing heat, the dark, experience freezing nights and carry all your gear!
Good job but more interesting facts please
i agree, i really need facts…
thank you for the facts. they were really helpful.
i like turtles
Me too cuz I’m a turtle lol
??????????????????????????????????
What is the population though??? and not namibia, the namib desert.
ya whats the population i cant find it anywhere
47,897
thank you this helped me with my school project
ayyyee….me too
this is kinda cool, but i needed more facts please
I have a school project and got assigned this desert. I need more facts please. I will get a B- if I don’t have 20 facts.
Then why not give us some facts/questions you would like answers to?
What is the population of the Desert Elephants and do they have any other name than “Desert Elephant”. How often do they reproduce? What is the general size of the Desert Elephant? Other than larger feet and the ability to survive on less water; what other facts make these elephants different?
Are there any people living thère like perhaps a tribe or a community or village and is there any human food any bandits or some kind of long distance trade